There are three types of questions in any language.
They are used:
1. To clear our doubts
2. To get some information
3. To get something confirmed
In grammar, they are called:
1. Inversion Questions
2. Interrogative Questions
3. Question-tag Questions
It is very easy to distinguish a question from a statement in the English language. If a sentence has an Auxiliary Verb before the subject you are sure that it is a question. Therefore before we go down to questions, we must learn English Auxiliary Verbs. Complete list of Auxiliary Verbs is given below.
Is, am, are, was, were
Will, would
Shall, should
Can, could
May, might
Must
Has, have, had
Need
Ought to
Used to
Dare
(Do, Does, Did)
———————————————————————————————————————————————
1. INVERSION QUESTIONS
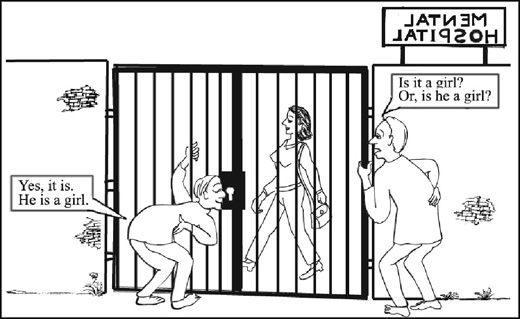
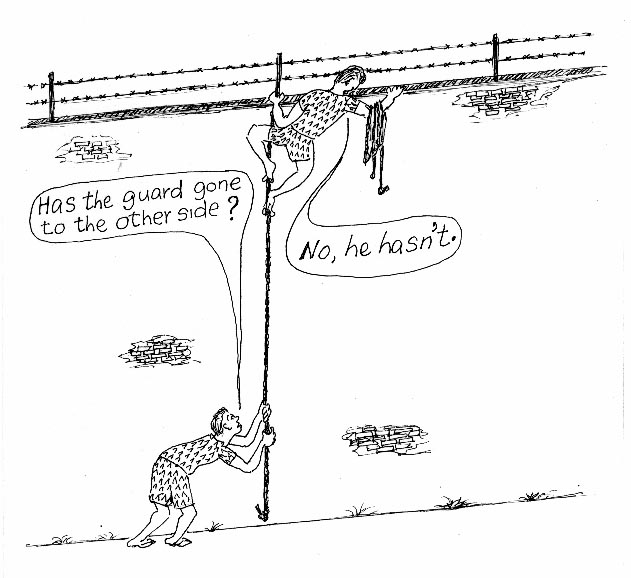
We use this type of questions to clear our doubts. We can make these questions by changing the word order of a statement. That is by placing the relevant auxiliary verb before the subject.
Statement = S+V.
Question = AV + S ?
Example:
He can swim. Can he swim?
She is ready. Is she ready?
Statements without Auxiliary Verbs take Do, Does or Did in questions.
*V1 plural takes ‘Do’
Example:
They like tea. Do they like tea?
*V1 singular takes ‘Does’
Example:
She goes to work by train. Does she go to work by train?
He works hard. Does he work hard?
Note:
You shouldn’t use ‘s’ or ‘es’ after the verb when you use ‘Does’ to make questions.
*V2 takes ‘Did’
Example:
He went there yesterday. Did he go there yesterday?
She returned home yesterday. Did she return home yesterday?
Note:
You shouldn’t use ‘V2’ when you make questions with ‘Did’.
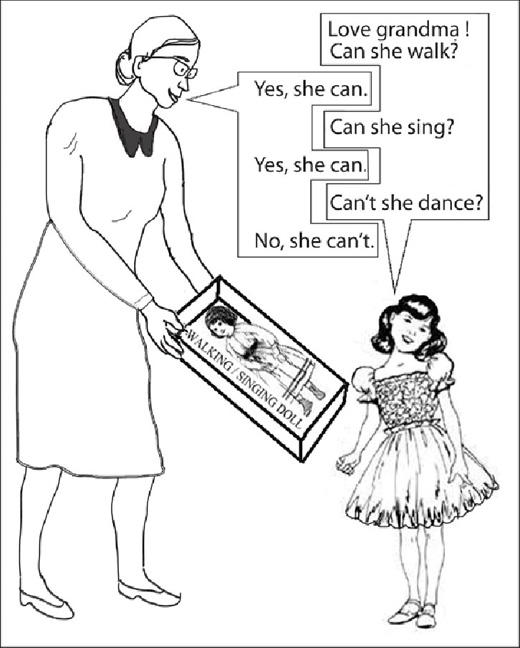
Look at these pictures and learn how to ask inversion questions and how to answer them. You must give short form answers beginning with ‘Yes’ or ‘No’.


———————————————————————————————————————————————
Negative statements and negative questions can be made using ‘Not’ after Auxiliary verbs.
Example:
He is there. He isn’t there.
Is he there? Isn’t he there?
He goes to work by bus. He doesn’t go to work by train?
Does he go to work by bus? Doesn’t he go to work by train?
———————————————————————————————————————————————
2. INTERROGATIVE QUESTIONS
To get some information we use questions beginning with question words. We call them ‘INTERROGATIVES’.
INTERROGATIVES:
WHO
WHOM
WHOSE
WHAT
WHICH
WHEN
WHERE
WHY
HOW
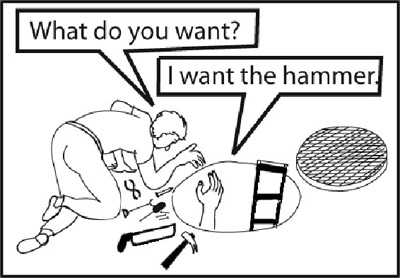
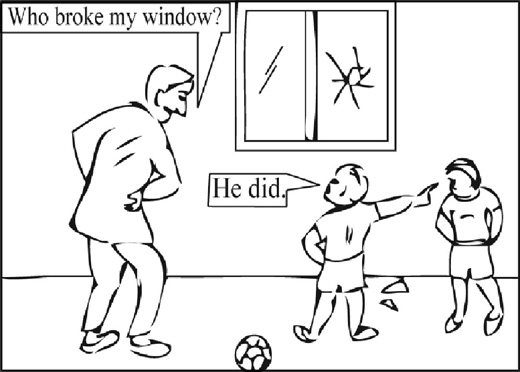
Interrogative questions can be made using a question word before an inversion question.
Example:
He came yesterday.
Did he come yesterday?
When did he come?
Note:
Questions about the subject need no inversion. Such questions can be made replacing the
subject with an appropriate question word in its place. The question words you can use to replace the subject are ‘WHO’, ‘WHAT’ and ‘WHICH’.
When you want to ask questions about the action, replace the verb with ‘DO’ and use ‘WHAT’ as the question word. The question about the action, given below, will be very useful for you for everyday use.
What will you do tomorrow?
What are you going to do?
What are you doing?
What have you done?
What did you do yesterday?
What were you doing when I came?
Look at these pictures and learn how to make and how to ask this type of questions.



———————————————————————————————————————————————
3. QUESTION-TAG QUESTIONS
We make a statement and immediately add a question-tag to get something affirmed. A question-tag has two parts, an auxiliary verb and a pronoun.
The rules are:
1. POSITIVE STATEMENT + NEGATIVE QUESTION-TAG
2. NEGATIVE STATEMENT + POSITIVE QUESTION- TAG
3. AUXILIARY VERBS REPEAT THEMSELVES IN THE TAG
4. OTHER VERBS TAKE ‘DO’, ‘DOES’ OR ‘DID’ IN THE TAG
Examples:
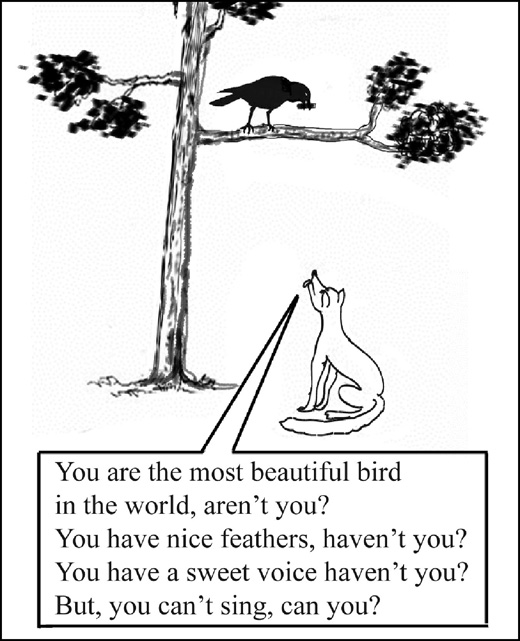
She can sing, can’t she?
She can’t dance, can she?
She loves fruit, doesn’t she?
She doesn’t like sweets, does she?
Now, look at these pictures and learn how to ask question-tag questions.


———————————————————————————————————————————————
Note: Answering questions
1. Short form answers beginning with yes/no for inversion questions. (Unstressed)
2. Long complete answers giving necessary information for interrogative questions.
3. Short form answers beginning with yes/no for question-tag questions. (Stressed)




